Introduction to CPL library
CPL library is a communications and topology management system for coupling any continuum fluid dynamics (CFD) solver to any molecular dynamics (MD) code. CPL library is free and open-source.
A full tutorial and example codes written in python, C++ and Fortran are provided with CPL library. Their purpose is to provide templates that are easily replaced by the user with any CFD or MD code of their choice.
If you'd like more details, or want to get started, please get in touch with us on the contact page; we'd love to hear from you and will help however we can.
The coupling approach with CPL Library
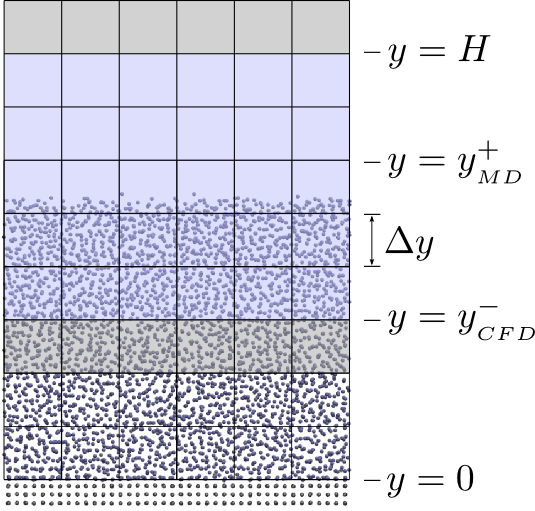
CPL library currently facilitates a domain-decomposition style of coupling. With this approach, a CFD program solves the continuum equations of motion in the upper region of a domain, and an MD simulation solves discrete-particle equations of motion in the lower region. The two programs exchange data (in this case with CPL library) to ensure selected field variables are consistent where the MD and CFD domains overlap.
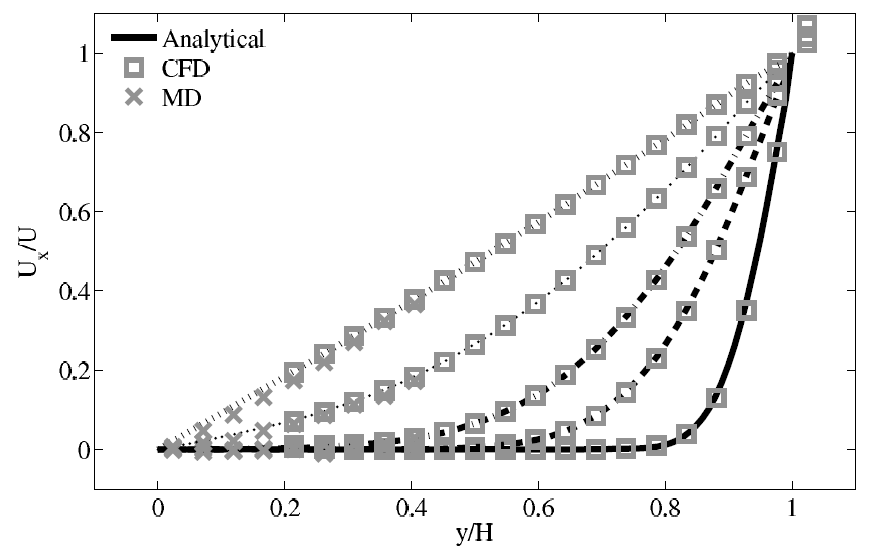
Some results of an example coupled simulation of planar-Couette flow (simple shear of a Newtonian fluid between two flat plates) can be seen in the videos below. The molecules have been coloured by their local streamwise velocity, and the velocity of the continuum field is shown by the colour of the solid plane at the edge of the domain.
The temporal evolution of the velocity field is consistent with the expected analytical solution for planar-Couette flow:
The possibilities for performing simulations beyond this canonical flow configuration are vast. For example, coupled simulations may be used to model the effect of complex wall textures in turbulent flows:
Supported Configurations
CPL library is written in Fortran with a C/C++ wrapper and is not expected to change much from its current form. The CFD and MD code are assumed to be massively parallel, running on a number of processors communicating through the message passing interface (MPI). The supported setup is a domain decomposition, with MD near the wall and CFD further away.
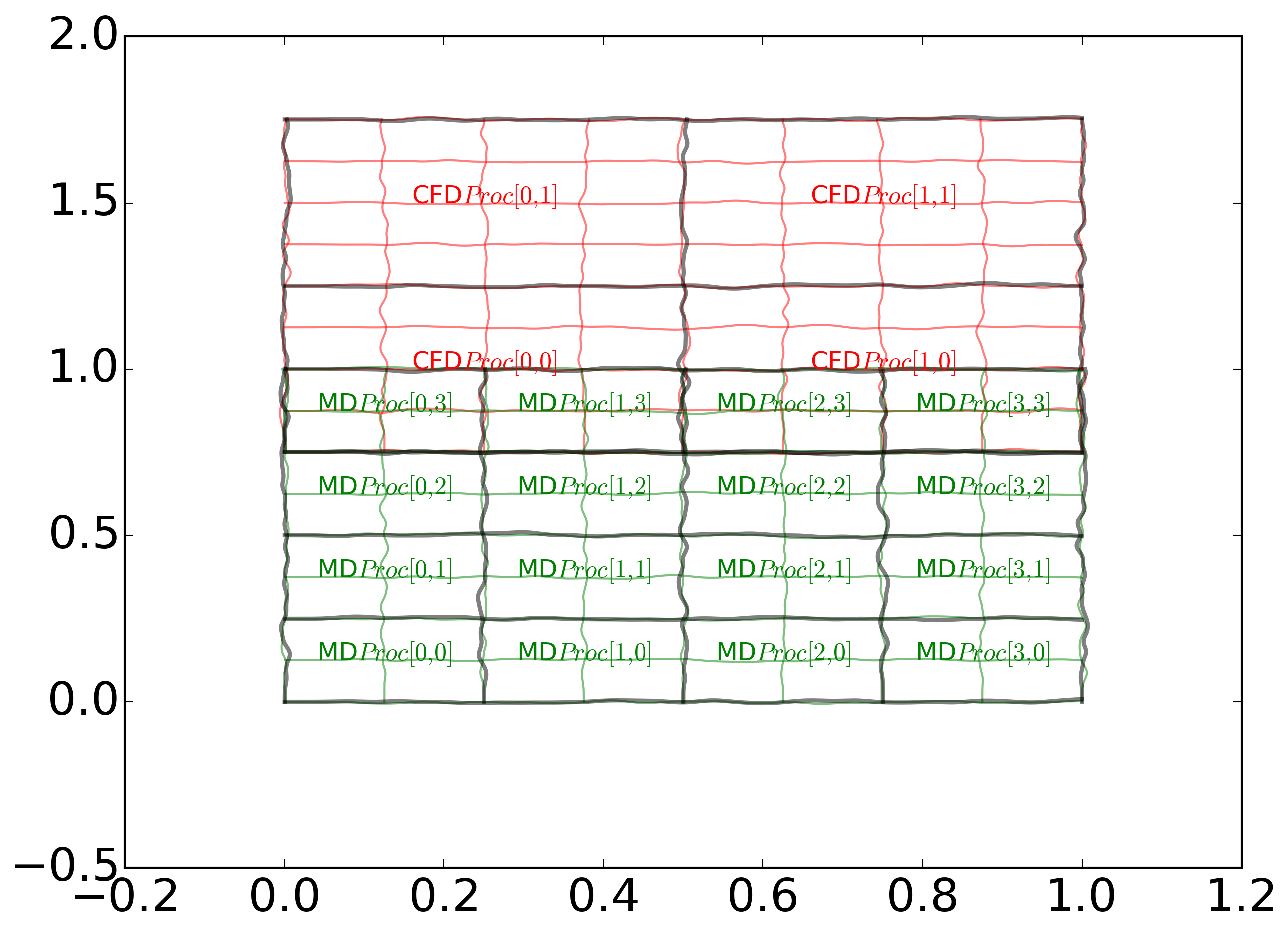
Currently this is the only case which is officially supported. In addition, the topological mapping assumes there is always at least one CFD processor to each MD and that processor boundaries align between the two codes (i.e. 2 CFD and 3 MD would not be supported). This setup is general enough to support, as a special case, complete overlap between the two codes.
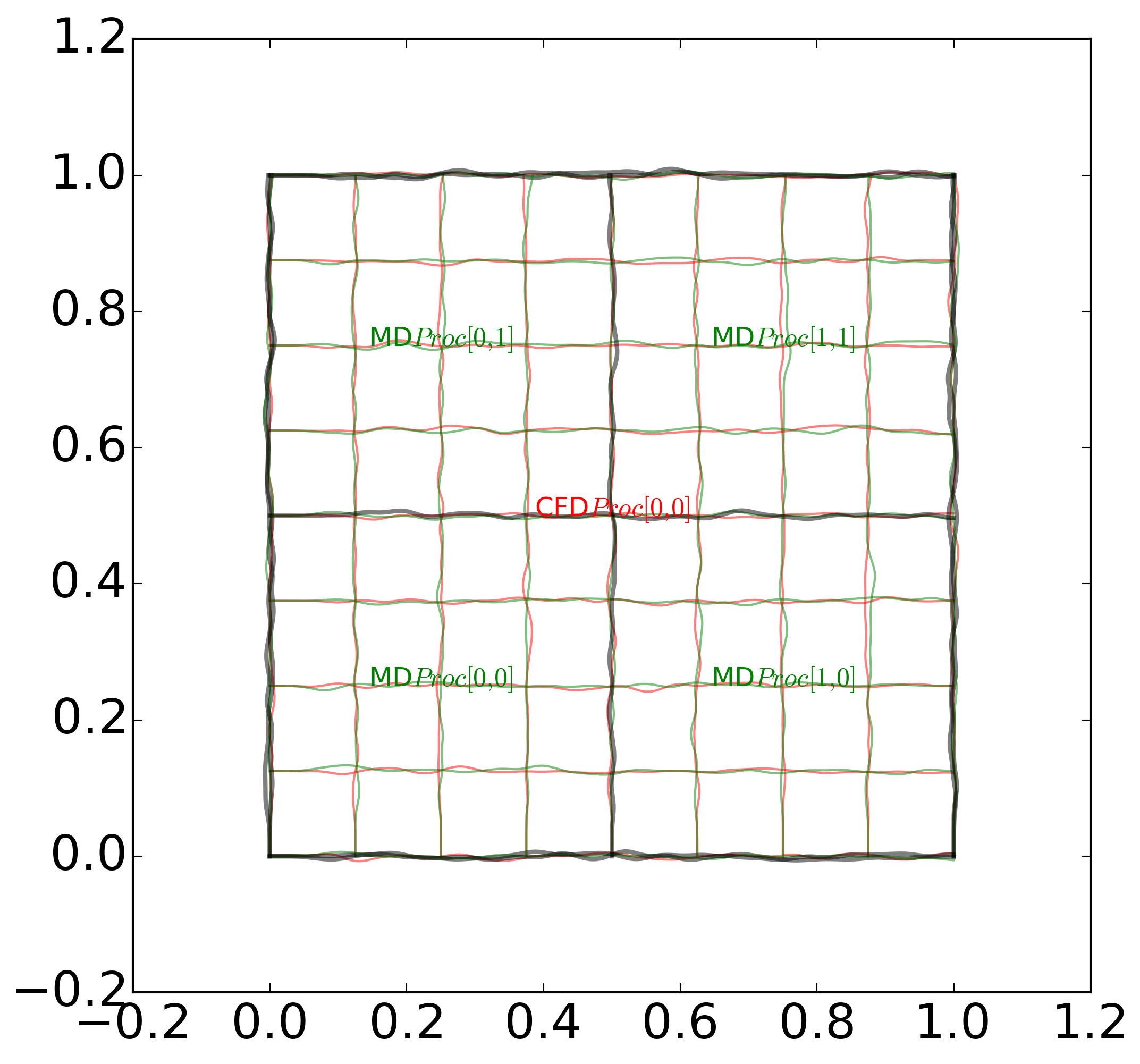
Despite this limitation, the design of the coupling software means that more complex cases, (e.g. non-uniform grids, multiple MD or CFD domains) can be accommodated by simply changing the mapping module of the coupler.